Understanding Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience and Its Impact on Usability Improvement

Published on: 10 May 2024 - Updated on: 10 May 2024 - Read 5882 times - Reading time: 38 minutes
Introduction
For a long time I have wanted to do a series of articles on the rules that guide our choices in our activity as business application developers . Whether it is Fitts', Hick's, Miller's or Jakob's laws, these concepts are unfortunately not necessarily known to the general public and, even worse, to certain agencies. I am therefore happy to be able to go into detail about this essential law of our activity: Law of User Experience or more commonly called Jakob's Law.
Introducing Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience
Jakob Nielsen , often recognized as a pioneer in the field of user interface ergonomics, formulated several essential principles intended to guide and improve the design of interactive systems. Among his most influential contributions is the Law of User Experience, a set of guidelines that aims to optimize the interaction between the user and the digital product.
Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience focuses on understanding how users interact with interfaces and provides methods to make those interactions as intuitive and efficient as possible. The central idea is that products should be designed with a deep understanding of user needs, expectations and behaviors. This involves a user-centered approach , emphasizing clear prioritization of information, simplified navigation and predictable interactions that meet user expectations without overwhelming or confusing them.
If today I share this information with you it is because, as the manager of a design office specializing in the development of business applications , I demonstrate that by applying these principles, designers and developers can create products that are not only functional but also enjoyable to use, contributing to a positive user experience that is crucial to a product's success in today's competitive digital environment. Jakob Nielsen posits that following these fundamental principles of user experience can significantly decrease error rates, reduce the learning time required to master a product, and improve overall user satisfaction. A daily leitmotif for our agency.
The principles set out by Nielsen are not merely theoretical but are the result of years of empirical observation and rigorous studies of how people use technology. This led to concrete recommendations that were widely adopted in the industry, making the law of user experience an indispensable pillar in the field of user interface design.
These principles continue to influence the way digital products are designed, ensuring that they remain accessible, understandable, and above all, useful to end users.
Importance of User Experience in Today's Digital World
It is clear that in the current digital landscape, saturated with technologies and choices, user experience (UX) has emerged as a determining factor in the success or failure of digital products . With fierce competition just a few clicks away, providing a great user experience is not just a nice-to-have, but a necessity.
The importance of user experience stems from its direct impact on user engagement and loyalty. A user-friendly and intuitive interface not only encourages faster adoption by new users but also builds trust and satisfaction among existing users . On the other hand, a bad experience can lead to increased churn and negative reviews, which can seriously damage a product's reputation and long-term viability .
In addition, an optimal user experience plays a crucial role in the digital transformation of companies. By improving the accessibility and usability of applications, businesses can not only reach a wider audience, but also increase operational efficiency and reduce customer support costs. For example, a well-designed user interface can decrease the need for extensive training and reduce user errors, leading to fewer support calls and increased productivity.
Taking user experience into account is also essential in building a positive brand image. Products that offer a pleasant and frictionless experience reflect a brand image that cares about its customers and is attentive to their needs. This perception can be a key differentiator in markets where products and services are often perceived as similar or interchangeable.
Finally, search engines such as Google have started using user experience as a criterion in ranking search results. Websites that load quickly, are easy to navigate, and are optimized for mobile devices tend to rank higher, which improves online visibility and attracts more traffic. This demonstrates that user experience optimization directly influences search engine optimization (SEO), making UX an essential part of digital marketing strategy .
In this constantly evolving digital environment, understanding and improving the user experience is therefore essential for any player seeking to stand out and prosper. Investment in quality UX thus becomes a central aspect of digital strategies, guiding development and marketing decisions in the digital age.
 PLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_PRIVACYHINTPLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_VIDEOLINK
PLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_PRIVACYHINTPLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_VIDEOLINK
Understanding Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience
Definition and detailed explanation of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience
The law of user experience, often associated with Jakob Nielsen, focuses on key principles that aim to optimize the ease of use and effectiveness of digital interfaces. Although Nielsen has formulated several specific laws and heuristics over the years, he is most recognized for his contributions to improving human-computer interaction through concise, end-user-focused rules.
One of the core principles of Nielsen's Law of User Experience is that "less is more" when it comes to user interface design . This principle suggests that interfaces should be simplified to eliminate any superfluous elements that do not directly support the user's tasks. The goal is to reduce users' cognitive load, allowing them to understand and use the interface more effectively.
Another central aspect of Nielsen's Law is the importance of consistency in user interfaces. The elements of an interface must be consistent not only in their aesthetics but also in their functioning. This means that similar elements should behave identically so that users do not have to relearn how to interact with different aspects of the same or similar systems. This uniformity helps users develop intuition about how the interface works, reducing learning time and increasing overall efficiency.
Nielsen also highlights the need for clear visibility into system status . Users should always be informed of what is happening through appropriate feedback within a reasonable time frame. This could include animations when loading content, confirmation messages after submitting forms, or warnings when errors occur. Transparency in interactions builds user trust and reduces frustration, allowing them to understand the underlying logic of the system.
In addition, Nielsen emphasizes flexibility and efficiency of use . Systems should be able to adapt to user experience, offering shortcuts or advanced functions for experienced users while remaining accessible to novices. This adaptability helps maximize usability by accommodating various learning styles and speeds, which contributes to a better overall user experience.
 PLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_PRIVACYHINTPLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_VIDEOLINK
PLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_PRIVACYHINTPLG_CONTENT_TWOCLICKYOUTUBEVIDEOS_VIDEOLINK
Each principle of Nielsen's Law has the ultimate goal of improving the quality of interaction between the user and the digital product. By integrating these principles into product design, designers can create more intuitive, engaging, and productive experiences for users , which is crucial in a competitive digital marketplace.
The Fundamentals of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience
Jakob Nielsen established several core principles that underpin his Law of User Experience, each targeting different aspects of interaction and interface design. These principles are designed to guide designers in creating digital products that are not only functional, but also intuitive and easy to use. Here are some of the key principles:
- Visibility of system status : The system should always keep users informed of what is happening, through appropriate feedback and in a timely manner. This can include loading indicators, order confirmations, update notifications, and more. The idea is to ensure that users never feel lost or unsure about the current state of their interaction with the system. Example: An e-commerce site displays a progress indicator during the checkout process, reducing users' uncertainty about the status of their transaction.
- Correspondence between the system and the real world : The system must speak the language of the users, with familiar words, phrases and concepts, rather than system-oriented terms. It should follow real-world conventions, making information presented logically and in a natural order. This helps users intuitively understand how to interact with the interface without requiring a steep learning curve. Example: A hotel reservation application uses easily recognizable calendar icons to indicate arrival and departure dates, using familiar visual conventions to simplify date entry.
- User Control and Freedom : Users often choose system functions by mistake and will need a clear "emergency exit" to exit the unwanted state without having to undergo an extensive process. Providing options to undo and redo actions gives users the flexibility to manage their interactions without fear of making irreversible mistakes. Example: A text editor provides clear options for undoing and redoing changes, allowing users to easily retrace their steps without losing data.
- Consistency and standards : Users should not have to wonder whether different words, situations or actions mean the same thing in different contexts. Following consistent design conventions and rules allows users to rely on their pre-existing knowledge to interact with a new interface. Example: All submit buttons on an application suite share the same design and position, increasing consistency and reducing confusion.
- Error Prevention : Even better than good error messages is careful design that prevents problems before they arise. For example, design elements that prevent users from making potential errors or features that automatically check the validity of user input contribute to a smoother and less frustrating experience. Example: An online form validates data formats as you type, preventing users from submitting incorrect information and having to start over.
- Recognition rather than recall : Minimize the user's cognitive load by making objects, actions and options visible. The user should not have to remember information from one part of the interface to another. Instructions for using the system should be visible or easily retrievable when needed. Example: Project management software displays icons and explanatory tooltips next to each feature to help users understand their usefulness without having to search for the information.
- Flexibility and efficiency of use : Interfaces should accommodate both inexperienced users and experts, allowing the latter to complete tasks more quickly. This can be achieved through customization or the ability to change default settings. Example: An email application offers a simplified interface for new users and advanced options for experienced users, such as automatic sorting rules and keyboard shortcuts.
- Aesthetics and minimalist design : Dialogues should not contain information that is irrelevant or rarely necessary. Each additional information in a competitive interface with relevant information and decreases their relative visibility. Example: Photo editing software features a clean interface, where advanced tools are grouped into drop-down menus, reducing visual clutter while making basic features easily accessible for beginners.
These principles, although simple in theory, require careful and thoughtful application in practice . They aim to create interfaces that not only meet users' needs but also improve their overall interaction with technology, making digital experiences more enjoyable and effective. By applying Nielsen principles, you can significantly improve usability by facilitating interaction between the user and the system, reducing errors and increasing efficiency and overall satisfaction .
The importance of principles in user interface design
The principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience play a crucial role in user interface design, guiding designers in creating products that are not only functional but also intuitive and accessible. Applying these principles is essential to meeting the expectations of modern users, who seek fast, simple and satisfying interactions with digital technologies. Here's how incorporating these principles positively impacts user interface design:
- Interface simplification : By following the principle of minimalism and clarity, designers can reduce visual noise and focus the user's attention on the most important information and actions. This helps users navigate the app or website more easily and complete their tasks with less effort and errors.
- Improving accessibility : By ensuring that systems speak the users' language and making information clearly visible, designers make their product accessible to a wider audience, including those who may have visual, hearing limitations or cognitive. This not only broadens the potential user base but also strengthens the inclusiveness of the technology.
- Increased efficiency : By allowing flexibility in the use of the interface, systems can adapt to the needs of various users, whether novice or expert. This adaptability allows all users to perform at their optimal level, thereby increasing the overall effectiveness of interaction with the system.
- Reduced learning time : When interfaces are designed for recognition rather than recall, users can intuitively navigate through them without having to remember specific commands or procedures. This decreases the learning time required to become proficient in using the system, which is particularly beneficial in environments where users frequently interact with multiple interfaces.
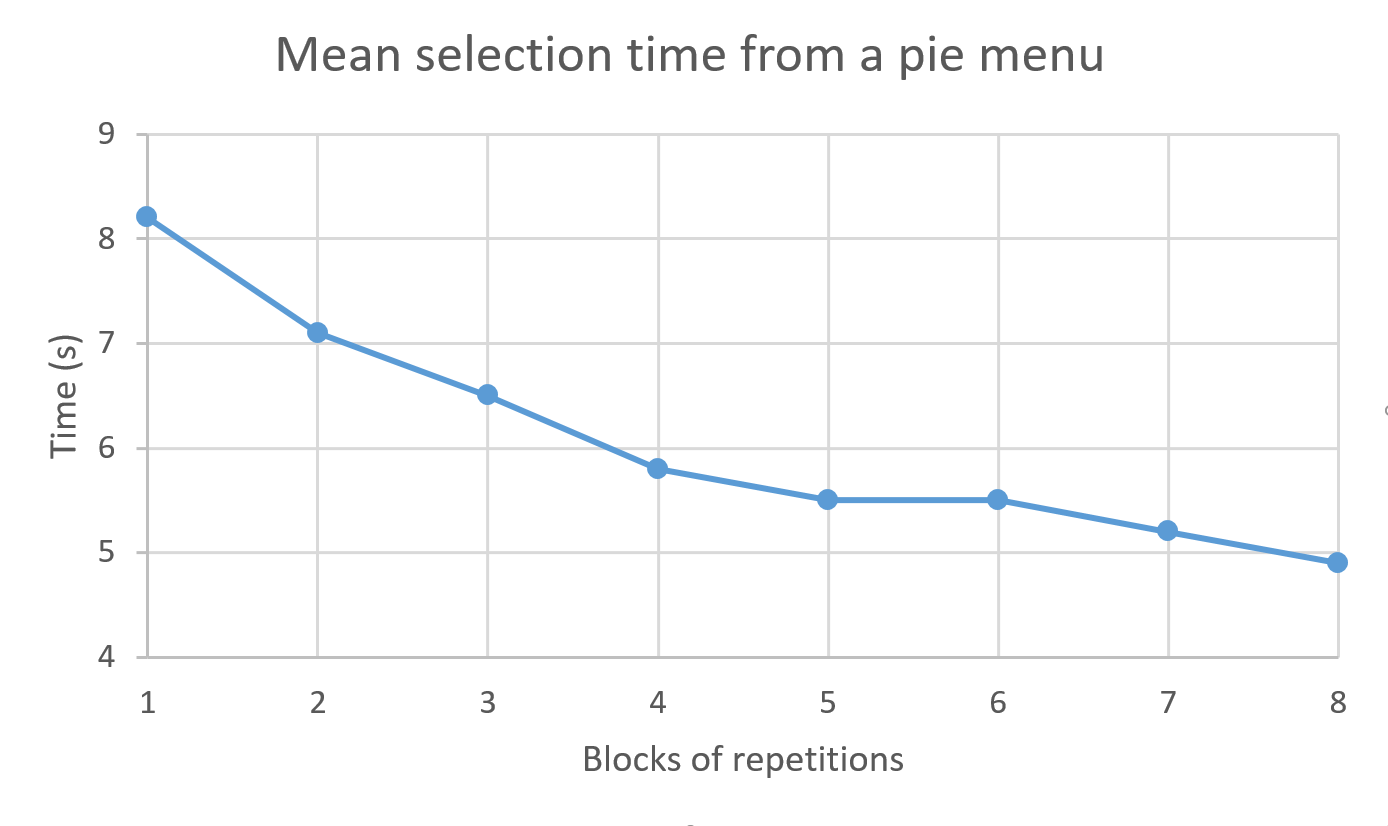 The study by Ahlstrom et al. had participants interact with the same menu interface for 8 different practice blocks: in each block, participants selected the same 6 items from the menu, and the resulting selection times were averaged to obtain the average time for this block. The learning curve shows that the average selection time decreases with practice.
The study by Ahlstrom et al. had participants interact with the same menu interface for 8 different practice blocks: in each block, participants selected the same 6 items from the menu, and the resulting selection times were averaged to obtain the average time for this block. The learning curve shows that the average selection time decreases with practice. - Error Prevention : By designing interfaces that anticipate potential errors and providing options to easily correct them, designers can prevent user frustration and improve overall satisfaction. This leads to lower support costs and a better reputation of the product in the market.
- Fostering Trust : Consistency in design helps build user trust. When interface elements behave predictably, users feel safer and more confident in their interactions with the system, which is essential for building a lasting relationship with the product.
By integrating these principles of the law of user experience into their projects, designers not only create products that work well; they create experiences that enrich users’ lives . This is all the more important in a context where efficiency, accessibility and convenience are common expectations of consumers of digital technologies.
Improving Usability thanks to the Law of User Experience
How Jakob's Law Helps Improve Usability
Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience provides a valuable framework for improving the usability of digital interfaces, making products more intuitive, efficient and enjoyable to use. Applying these principles helps create systems that better meet user needs and expectations , which is essential to ensuring high adoption and user satisfaction. Here are some ways Nielsen's Law improves usability:
- Clarifying interactions : By minimizing interface complexity and eliminating unnecessary elements, the law encourages the creation of clean designs that do not confuse users. This makes it easier to understand the available features and helps users make decisions faster, improving the overall experience.
- Process standardization : Consistency is another key principle that improves usability. By maintaining a consistent design across different sections of a product, users can transfer their knowledge from one part to another without relearning how to interact with the interface. This reduces the time needed to get used to a new system and lowers the learning curve.
- Improved navigation : By following the law of user experience, designers can structure menus and options in a logical and intuitive way, guiding users through task flows with fewer errors and frustrations. Good navigation makes it easier for users to move around an app or website, which is crucial to their effectiveness.
- User Adaptation : By offering flexible interfaces that adapt to the user's skills, whether novice or expert, the law helps personalize the user experience. For example, shortcuts and advanced commands can be offered to experienced users, while wizards and tutorials can guide new users, making the system accessible to everyone.
- Error Prevention and Reduced Support Costs : By anticipating common errors and preventing them before they happen, systems designed using Nielsen principles reduce opportunities for user frustration. This not only improves the user experience but also reduces the need for external assistance to resolve issues, which can lead to significant savings in customer support.
- Effective feedback : Ensuring that users receive clear and immediate feedback after their actions is essential for good usability. Whether through visual or audio confirmations, progress indications, or error alerts, effective communication between the interface and the user helps maintain a confusion- and error-free interaction.
By integrating these aspects into digital product design, the principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience facilitate the creation of interfaces that not only meet user expectations but often exceed them, thus promoting greater satisfaction and user loyalty.
Real-world examples of improving usability using Jakob's Law
Applying the principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience has led to many tangible improvements in user interface design. These principles, when applied correctly, can transform complex and frustrating user experiences into fluid and intuitive interactions. Here are some concrete examples where the application of these principles has significantly improved the usability of digital products:
- Simplification of the e-commerce interface : An e-commerce site revised its checkout process following the principle of minimalism and clarity. Initially, the process had several unnecessary steps and requested redundant information, which lengthened transaction times and increased cart abandonments. By simplifying the checkout page to contain only essential fields and grouping similar steps together, the site significantly reduced checkout time and increased the conversion rate.
- Task Management Mobile App Improvement : A popular task management app has incorporated principles of flexibility and efficiency of use by adding customizable shortcuts for frequent users. These shortcuts allow power users to navigate the app more quickly and perform common tasks with fewer clicks. This not only improved the experience for advanced users but also kept the interface simple for new users.
- Online Reservation System Redesign : An online reservation system for a hotel chain was redesigned to better match the real world, using familiar terms and metaphors that users intuitively understand. Instead of using technical jargons or abstractions, the new design uses clear images and simple language to guide users through the booking process, which has reduced the error rate and increased customer satisfaction.
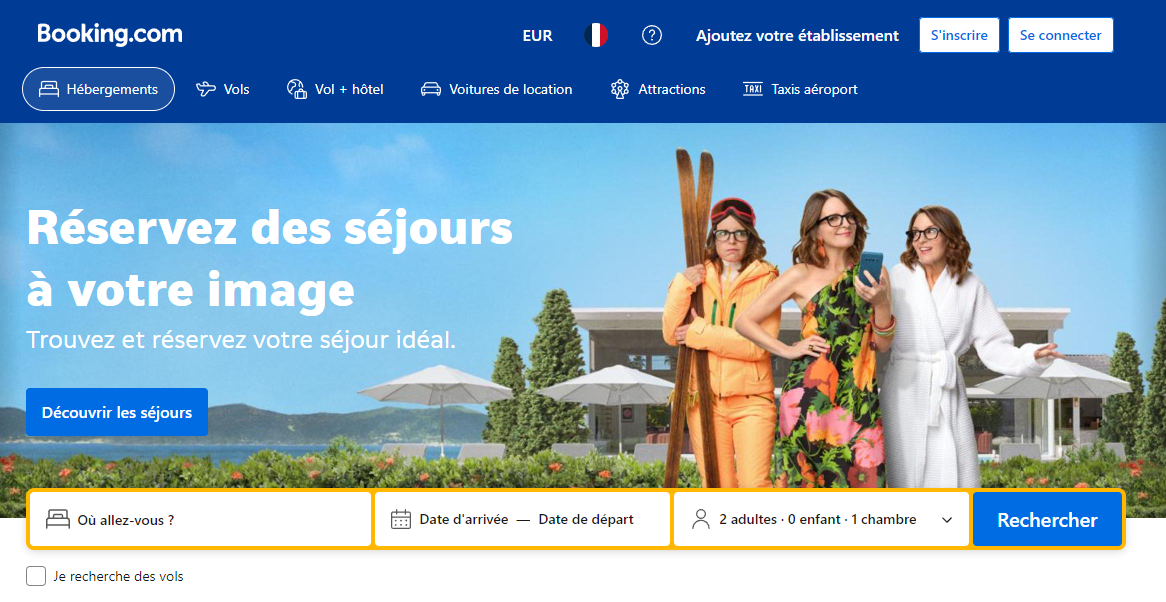 Even after its redisgn and a change of wording, the Booking.com reservation site has retained the constants of a reservation site: a search engine located in the middle of the page and connection buttons in the header.
Even after its redisgn and a change of wording, the Booking.com reservation site has retained the constants of a reservation site: a search engine located in the middle of the page and connection buttons in the header. - Optimization of the interface of medical software : Software used by healthcare professionals has been revised to prevent errors by adding entry confirmations and automatic data checks. Previously, input errors were common and could lead to complications in treatments. By integrating data validations and clear error messages, the software helped minimize these errors, improving patient safety and healthcare professional efficiency.
- Government Administration Portal Redesign : A government portal has been restructured to improve visibility of system status and recognition rather than recall. Changes included progress indicators for ongoing requests, restructured menus to reflect frequent actions, and context-sensitive help for complex form fields. These changes made the portal more intuitive, reducing the need for phone support and improving user efficiency when navigating the system.
Each of these examples illustrates how Nielsen principles can be implemented to solve specific usability problems, leading to measurable improvements in both user performance and overall satisfaction . These improvements demonstrate the effectiveness of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience in making digital products more accessible and enjoyable to use .
Link between good use and better user experience
The effectiveness of use, or usability, of a digital product is directly linked to the quality of the user experience. This connection is crucial because it not only affects user satisfaction, but also their willingness to continue using the product and recommend it to others. Good usability reduces barriers to interaction, allowing users to complete their tasks efficiently, satisfactorily, and without frustration.
- Task Ease and Error Reduction : A well-designed interface allows users to easily navigate and complete desired tasks without errors or delays. When users can achieve their goals quickly and without obstacles, it creates a positive impression that builds their confidence in the product. For example, project management software that allows users to create, assign and track tasks with a few clicks simplifies the project management process. Intuitive features, like drag-and-drop to reorder tasks and automatic notifications for deadlines, increase efficiency and reduce the risk of errors or omissions.
- Improved user retention and loyalty : Good usability means that users can learn to use the product more quickly, decreasing their frustration and increasing their overall satisfaction. This leads to greater user loyalty and retention, as they are less likely to look for alternatives. For example, an e-commerce mobile app that offers a smooth browsing experience, fast loading times, and search Effectively encourages users to come back and make repeat purchases, rather than turning to competitors.
- Increasing accessibility : When products are designed to be usable by people with varying abilities and skill levels, they become more accessible to a wider audience. This not only increases the market potential of the product, but also promotes inclusiveness. For example, a website that follows the Web Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) by providing text alternatives for images, ensuring good contrast of colors, and by allowing keyboard navigation, not only improves its usability but also becomes accessible to users with visual or motor disabilities.
- Impact on satisfaction and word-of-mouth promotion : Satisfied users are more likely to share their positive experiences with others, whether through online reviews, personal recommendations, or on social media. This word-of-mouth promotion can be a powerful growth driver for the product. For example, a video streaming service with a user interface that effectively recommends new content based on previous preferences can improve user engagement and encourage positive discussions and recommendations on social platforms.
By integrating good usability into product design, companies are not only doing their users a favor; they engage in a beneficial, long-term strategy that improves user satisfaction, increases retention, and promotes organic growth through positive referrals.
Reducing Learning Time with the Law of User Experience
How the law helps reduce learning time for users

Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience provides essential guidelines for designing interfaces that not only capture users' interest but also simplify their learning curve. By incorporating the principles of this law, designers can create products that are intuitive and easy to master , allowing users to become proficient more quickly . Here's how implementing these principles can significantly reduce learning time:
- Consistency and Standards By maintaining consistency in interface elements, users learn faster because they don't have to rediscover how similar actions work each time. When buttons, actions, and behaviors are standardized across the interface, users can transfer their acquired knowledge from one part of the system to another without additional effort. For example, in a software suite, if the process for saving A document is the same in all programs (for example, a save button in the upper right corner), users can move from one software to another without having to relearn this fundamental functionality.
- Visibility of system state: Providing users with clear feedback on what is happening with the system helps them understand the behavior of the interface without confusion. If users receive immediate feedback in response to their actions, such as loading animations or visual confirmations, this reduces the time it takes to learn how to use the system effectively. For example, an e-commerce site that immediately displays a visual message when an item is added to the cart allows users to instantly understand that their action has been taken into account without having to check elsewhere.
- Error prevention: Designs that actively prevent errors can drastically reduce the time new users spend understanding and correcting problems. By anticipating common errors and guiding users in the right direction from the start, designers can remove barriers to learning. For example, an input form that uses real-time data validation to correct errors like Poorly formatted phone numbers help users understand system expectations without frustrating trial and error.
- Recognition rather than recall: Designing interfaces where needed information is visible or easily retrievable helps users focus on using the application rather than recalling hidden information. Minimizing the need to remember information from session to session speeds up the learning process. For example, in project management software, displaying a list of shortcuts or common commands directly on the main screen allows users to use them efficiently without having to memorize them.
- Flexibility and efficiency of use: Systems that offer shortcuts and adaptations for experienced users while remaining accessible to beginners allow all users to work more efficiently from the first contact with the product. Interfaces that adapt to different skill levels facilitate gradual and efficient learning. For example, a text editor that offers a 'basic' mode for new users with simplified functionality, while allowing easy switching to a mode 'Advanced' with more complex options, helps users progress at their own pace.
By applying these principles, products become more accessible and easier to learn, significantly reducing learning time and improving the overall user experience. These improvements allow users to feel competent and confident in using the product from the first interactions.
Importance of reducing learning time for better user experience
Reducing learning time in using digital products is a crucial goal of user interface design, directly linked to a positive user experience. When users can master a product quickly and easily, their initial satisfaction and long-term commitment to the product are significantly improved . Here's why reducing learning time is essential:
- Increased user efficiency: When users quickly learn to navigate an interface, they can achieve their goals more efficiently. This is especially important for business applications where time is a precious resource. A user who can master a tool quickly is more productive and more likely to take full advantage of it. For example, accounting software that walks new users through its features with an interactive tutorial or tooltips helps reduce the time of learning, allowing businesses to benefit more quickly from its advanced features.
- Reduced frustration and abandonment: A long learning process can be a source of frustration for users, who may feel discouraged if the interface is too complex or poorly designed. Reducing barriers to learning minimizes the risk of users abandoning the product out of frustration. For example, a video streaming service that allows users to quickly understand how to find and watch movies through intuitive design and clear instructions, decreases the chances of users abandoning the service due to unnecessary complications.
- Improved accessibility: Products that are easy to learn are also more accessible to a wide range of users, including those who may not be technically savvy. This is crucial for apps aimed at a diverse audience, where technical skills can vary widely. For example, a mobile health app that simplifies its interface and uses clear language can help older adults understand how to monitor their daily health, making the app more accessible and useful for this demographic.
- Encouraging product adoption: Products that are easy to learn are often more quickly adopted by the market. Ease of use can become a major selling point, especially in saturated markets where users have many options. For example, a photo editing app that offers advanced editing features while maintaining a learning curve low through pre-made templates and a drag-and-drop interface, quickly attracts users who want professional results without the complexity of traditional photo editing tools.
- Promoting user retention: When users feel like they can master an app quickly, they are more likely to feel satisfied with their choice and continue using the product over the long term. Competence in using a product builds user confidence and brand loyalty. For example, email marketing software that offers step-by-step guides for creating campaigns can transform even a novice user into a confident professional, encouraging continued use and loyalty to the platform.
In sum, reducing learning time is a critical strategy for improving user experience, encouraging product adoption and retention, and ultimately leading to broader commercial success for digital product developers.
Real-world examples where reducing learning time improved user experience
Reducing learning time is a key factor in designing successful user interfaces, directly impacting user adoption and satisfaction . Here are several real-world examples from various industries where minimizing learning time has significantly improved the user experience:
- Content Management Platforms (CMS) : In its version 5, Joomla, a popular CMS, introduced an intuitive dashboard with interactive guides for new users, which explain step by step how to create and publish content. This approach allowed users without prior technical skills to get started quickly, reducing learning time and increasing user satisfaction, leading to a significant increase in product adoption.
- Mobile banking apps : One bank redesigned its mobile app user interface to make it more intuitive, using clearly labeled icons and simplified navigation. New features, such as check photography for deposits and tutorials for frequent transactions, allowed customers to quickly understand how to use the app without assistance. This not only improved customer satisfaction but also reduced customer support costs.
- Educational Software : An educational software developer has implemented interactive tutorials and personalized learning paths into its app, allowing students of all ages to progress at their own pace. Instant feedback on exercises and clear explanations of difficult concepts helped reduce learning time, making the app more engaging and increasing user retention rates.
- Graphic Design Tools : A graphic design tool aimed at non-professionals introduced a series of predefined templates and a 'drag and drop' interface, allowing users to create complex designs without prior design knowledge. This simplification allowed users to produce professional results quickly, which improved the overall user experience and expanded the product's user base.
- Hospital Information Systems : A hospital information system was redeveloped to incorporate a more intuitive user interface, with simplified menus, uniform icons, and better integration of reporting features. Doctors and nurses were able to access critical patient information more quickly, reducing the time spent navigating the system. This has not only improved operational efficiency but also contributed to better healthcare outcomes.
These examples illustrate the significant impact that reducing learning time can have on efficiency, satisfaction, and user engagement in a variety of contexts. By facilitating quick access to key features and minimizing barriers to effective use, designers can create products that better meet user needs and are adopted more widely.
Reduced Frustration and Abandonment thanks to the Law of User Experience
How the law helps reduce user frustration and abandonment

Applying the principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience plays a crucial role in reducing user frustration and abandonment. These principles help create more intuitive interfaces, reducing errors and misunderstandings that can lead to frustration and ultimately product abandonment. Here's how incorporating these principles can actually improve the user experience:
- Clarity and simplicity: Following the principle of simplicity, the interfaces are designed to be as clear and understandable as possible. This means avoiding visual clutter, minimizing technical jargon, and presenting information in an organized and logical manner. A clean interface allows users to navigate easily, reducing the chances of frustration due to confusion or inability to find essential features. For example, a travel booking app simplifies its booking process by clearly displaying options. filtering, flight information, and steps needed to finalize a reservation, avoiding user frustrations that can arise when navigating complex or poorly designed interfaces.
- Immediate Responses and Appropriate Feedback: Systems must provide immediate responses to user action, whether through success messages, error messages, or progress notifications. Quick feedback assures users that their actions have been recorded and guides them to the next step, reducing uncertainty and frustration. For example, an e-commerce site uses animations and confirmation messages when adding items. items to cart, providing users with immediate visual feedback that confirms their action was successful, reducing frustration and the possibility of abandonment.
- Consistency and predictability: By maintaining consistency across the interface, users learn system patterns and behaviors more quickly, making using the product more intuitive. When users know what to expect from the interface, they are less likely to make mistakes and feel frustrated. For example, a personal finance app maintains a consistent layout and functionality across its different pages. , allowing users to predict the location of controls and application reactions, minimizing confusion and error.
- Accessible Help and User Support: Providing easily accessible help options, like built-in FAQs, tutorials, or live support, can significantly reduce user frustration. Immediate support helps resolve issues quickly before they lead to abandonment. For example, video editing software provides quick access to online support and tutorial videos right from the user interface, enabling users to find solutions to their problems without leaving the workflow, thereby improving the continuity of the user experience and reducing the risk of abandonment.
By incorporating these principles, products are not only easier to use, but they also become less likely to cause user frustration. This leads to a more satisfying experience and a higher adoption rate , with a significant decrease in abandonment rates.
Link between frustration, abandonment and user experience
Frustration and abandonment are closely related in the context of user experience. When users encounter obstacles or complications while using a product, their frustration increases, which can often lead to product abandonment . Understanding this dynamic is crucial for interface designers because it highlights the importance of creating smooth, frictionless user experiences. Here's how frustration relates to abandonment and its impact on user experience:
- Friction points : Friction points in using a product, such as complicated navigation processes, slow loading times, or frequent errors, can all increase user frustration. This frustration is often the first step toward abandonment, especially if the user feels that the solution to their problem is too complex or inaccessible. For example, in an online reservation application, if users cannot easily change the dates or travel options without starting the booking process again, they may become frustrated and choose to leave the app in favor of a more user-friendly alternative.
- Impatience and Modern Expectations : In the digital age, users have high expectations for performance and efficiency. The slightest disappointment or delay can lead to loss of patience and disengagement. How quickly a product responds to user orders is therefore a key factor in avoiding frustration and abandonment. For example, on an e-commerce site, slow loading times when adding items to cart can frustrate users who expect instant gratification, causing them to abandon their purchases.
- Errors and lack of support : When users make mistakes or don't understand how to proceed, the lack of clear, accessible support can increase their frustration. Effective user support and helpful error messages are essential to keeping users engaged and satisfied. For example, a financial software user who receives cryptic error messages without clear directions for fixing them may feel frustrated and less inclined to continue using the software.
- Unnecessary complexity : A design that is not intuitive or requires unnecessarily complex interactions can also increase frustration. Products should be designed so that common tasks can be accomplished quickly and easily. For example, a digital camera with a complicated user interface may discourage non-professional users, who may not understand how to access basic features like zooming or changing shooting modes, leading to frustration and potentially abandoning the device for a simpler alternative.
By analyzing these interactions between frustration and abandonment, it is clear that minimizing friction points, improving response times, providing adequate support, and simplifying the interface are key steps to improving user experience . Reducing frustration can not only decrease abandonment but also increase user satisfaction and loyalty, which is essential for the long-term success of a product .
Real-world examples where reducing frustration and abandonment improved user experience
Reducing frustration and abandonment is a crucial goal for improving user experience and, therefore, the overall success of a product. Here are real-world examples that illustrate how different companies have improved user experience by minimizing these two negative factors:
- Optimization of the interface of an e-commerce site : An online sales site noticed a significant drop in the cart abandonment rate after simplifying its checkout process. By reducing the number of pages and actions required to complete a purchase and integrating quick payment options, the site not only reduced the frustration of a long and complex process, but also increased the conversion rate. Case in point: By allowing users to save payment information and select pre-configured shipping options, the time it took to checkout was reduced, leading to a decrease in cart abandonment and an increase in repeat sales.
- Improving the user interface of a mobile banking application : A bank revised the interface of its mobile application to make transactions more transparent and information more accessible. By improving navigation and providing clear explanations for each transaction type, the app has reduced user errors and, therefore, the frustration associated with mobile banking. Case in point: Adding intuitive filters to view transaction histories and implementing an instant confirmation system for transfers and payments increased user confidence in the app, reducing calls to customer service and improving the overall user experience.
- Content Management System (CMS) Redesign : A popular CMS has been updated to provide a more intuitive user experience, especially for new users. The redesign included a cleaner interface, integrated tutorials, and better online support. These improvements helped reduce the abandonment rate among new users, who were previously frustrated by the complexity of the platform. Case in point: Introducing a customizable dashboard that walks users through the most used features and helps them understand how to configure their site significantly improved engagement and reduced the number of people leaving the platform soon after registration.
- Simplifying a travel booking tool : An online travel booking service has revised its user interface to eliminate ambiguities in the flight and accommodation selection process. By making cost and availability information immediately visible and easily understandable, the tool reduced frustration for users who previously had to navigate through multiple screens to obtain these details. Case in point: Adding an interactive calendar view that clearly shows the cheapest days to travel allowed users to make more informed decisions quickly, increasing satisfaction and reducing the chances of abandoning mid-trip. reservation.
These examples clearly show that well-designed user interfaces that are responsive to user needs can significantly reduce frustration and abandonment, leading to an improved user experience and greater business success. By focusing efforts on eliminating friction points and simplifying processes, businesses can build a broader, more satisfied customer base.
Better SEO thanks to a Good User Experience
Link between good user experience and better SEO
In the field of web development, the relationship between good user experience (UX) and search engine optimization (SEO) has become increasingly significant. Search engines like Google have gradually incorporated UX-related criteria into their ranking algorithms , recognizing that sites with better user experiences deserve increased visibility in search results. Here's how a good user experience can positively influence a site's SEO:
- Page Load Time : The loading speed of a website is a key UX factor that directly affects SEO. Search engines favor sites that load quickly because a slow loading time can frustrate users and cause them to leave the site before the page has even fully loaded. By optimizing images, minimizing JavaScript code, and using content delivery networks (CDNs), webmasters can improve loading speed and, therefore, both UX and SEO. For example, an e-commerce site reduces its page loading time from 6 seconds to 2 seconds. This improvement will not only increase conversion rates but will also contribute to a better position in Google search results. The results are measurable and the impact is rapid.
- Mobile-friendly design : With the increase in the use of smartphones to access the internet, having a responsive design that works well on all devices is crucial for UX. Google uses mobile-friendliness as a ranking criterion, penalizing sites that are not optimized for mobile devices. A responsive interface improves mobile user experience and promotes higher rankings in mobile searches.
- Click-through rate (CTR) and session duration : Good UX design attracts and retains users on a site. Clear headlines, informative metadata, and intuitive navigation can increase click-through rates from search engine results pages, as well as site session duration, both important metrics for SEO. Higher CTRs and longer sessions signal to search engines that the content is relevant and valuable to users, which can improve site rankings. For example, redesigning a news site that incorporates rich snippets and optimized title tags is likely to significantly increase the CTR of its pages in search results.
- Bounce rate : A high bounce rate often indicates a poor user experience, which could be due to irrelevant content, poor navigation, or slow-loading pages. By improving the UX, sites can reduce their bounce rate, signaling to search engines that the site is high quality and deserves higher rankings.
These aspects of UX play a direct role in boosting a website’s visibility on search engines. Meticulous attention to user experience results not only in better user satisfaction and retention but also in a significant improvement in SEO , creating a virtuous cycle of traffic and engagement.
How the Law of User Experience Can Help Improve SEO
Applying the principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience can have a significant impact on a website's SEO. These principles aim to make sites more usable, accessible and enjoyable, which directly aligns with the factors that search engines use to judge the quality of a site. Here's how incorporating these principles can improve SEO:
- Improved accessibility and navigability : Search engines favor sites that are easily accessible and navigable for users, including those with disabilities. Applying the principle of accessibility can include the use of ALT tags for images, clear titles, and a logical content hierarchy that helps search engines better index pages. For example, a recipe site implemented detailed ALT tags for all its images and structured its articles with appropriate headers, thereby improving its accessibility and indexing by search engines, leading to an increase in organic traffic.
- Optimizing page loading times : Loading speed is a well-known SEO factor. Improving loading speed by reducing image weight, optimizing scripts, and using caching can reduce loading time and decrease bounce rate, a positive signal for search engines. For example, an online store cut its loading time in half by optimizing its images and using a content delivery network (CDN), which not only improved its SEO ranking but also increased its conversions.
- Responsive design : A responsive design that works well on mobile devices and tablets is essential for good SEO, especially since Google started indexing mobile versions of sites first. Sites that provide a good user experience across all devices tend to rank higher. For example, after updating its site to be fully responsive, an online magazine saw a significant improvement in its positioning in mobile search results, leading to a 40% increase in mobile traffic.
- Improving User Engagement : By improving the usability and interactivity of sites, consistent with Nielsen principles, sites can increase user time spent and engagement. Search engines interpret long session time and high interactions as indicators of quality content. For example, a news site introduced interactive elements such as videos and infographics, increasing the average time spent on page. This was viewed positively by search engines, who saw these interactions as a sign of engaging and relevant content.
By implementing these principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience, websites not only serve their users better; they also improve their visibility and ranking in search engines. This shows that SEO and UX are intrinsically linked , and that improving one can have significant positive impacts on the other.
Real-world examples where a good user experience led to better SEO
A good user experience (UX) is essential not only to satisfy a site's visitors but also to improve its positioning in search engines. Many cases illustrate how improving UX led to better search engine optimization (SEO). Here are some concrete examples that demonstrate this relationship:
- E-commerce site : An online retailer redesigned its site to make it more user-friendly, improving product searches and optimizing product descriptions and images. This improvement not only made navigation easier for users but also allowed better indexing by search engines. As a result, the site saw an increase in its organic traffic and an improvement in its conversion rate. For example, implementing structured product tags and reducing page load time improved the site's visibility in product searches, increasing both user sessions and sales.
- Media Content Platform : A video content platform optimized its user experience by improving the quality of its videos, reducing loading times, and making the site fully responsive for mobile devices. These changes not only increased user engagement but also improved the site's ranking in search results, since search engines favor sites that provide a good mobile experience. For example, after these changes, the site saw a significant increase in average time spent per page and a decrease in bounce rate, clear signs of an improved user experience, which contributed to better visibility in search results. video.
- Tourist Information Portal : A website intended to promote tourism has been redesigned to include interactive maps, personalized recommendations, and downloadable travel guides. These improvements made the site more useful and engaging for users, which increased time spent on site and reduced bounce rate. The consequence was higher rankings in tourism-related searches. For example, the use of rich content such as videos and photo galleries, as well as the integration of user comments, improved the interactivity of the site, which was favorably evaluated by search engines, resulting in an increase in the visibility of the site on competitive search terms.
- Financial services app : An app offering financial services has revamped its user interface to make information more accessible and transactions more transparent. The clarity and ease of use reduced user errors and frustrations, which encouraged more frequent and longer visits. This UX improvement was well received by search engines, which improved the app's ranking in search results related to financial services. For example, simplifying the registration process and improving visual security increased user trust, which increased engagement and reduced transaction abandonments, thereby improving SEO through engagement signals strong user.
These examples clearly show that efforts to improve user experience can have a direct and positive impact on SEO. By providing a superior user experience, sites can not only retain their visitors but also improve their visibility and positioning in search engines.
Conclusion
There is a lot to say about this Jakob law, so it is time to conclude by going over the essential ideas and hoping that this memo will help you keep the important content in mind.
Summary of key points covered in the article
In this article, we explored Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience in depth, highlighting its significant impact on improving the usability of digital interfaces. Here is a summary of the key points covered, illustrating how the application of this law can positively transform design and user interaction:
- Presentation of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience : We introduced the Law of User Experience, highlighting Jakob Nielsen's approach which favors simplicity and efficiency to optimize user interactions with digital systems. The law focuses on understanding user behaviors to create interfaces that intuitively meet their needs.
- Importance of User Experience in Today's Digital World : User experience is crucial in digital product design as it directly influences user satisfaction and loyalty. A good user experience can lead to better product adoption and increased competitiveness in the market.
- Definition and detailed explanation of the law : We have defined Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience and explained its fundamental principles. This section allowed us to understand how each principle contributes to reducing the complexity and improving the accessibility of interfaces.
- The fundamental principles of the law : Principles such as visibility of the system state, error prevention, and flexibility and efficiency of use were discussed. These principles help designers create interfaces that anticipate and respond to user needs.
- Improving Usability with the Law of User Experience : Concrete examples have shown how the application of the law can improve the usability of products, facilitating simpler interactions and reducing the time needed to complete tasks. tasks.
- Reducing learning time with the Law of User Experience : The impact of the law on reducing learning time was illustrated, showing how intuitive interfaces allow users to quickly master systems, thereby increasing their efficiency and their satisfaction.
- Reducing Frustration and Abandonment with the Law of User Experience : This section detailed how the law helps minimize user frustration and reduce abandonment rates, creating positive user experiences that encourage continued commitment and loyalty.
- Better SEO through Good User Experience : We looked at the connection between good user experience and better SEO, discussing how search engines favor sites that offer great UX, resulting in higher rankings in search engines. search results.
Each section of this article has tried to highlight the crucial importance of following Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience to design interfaces that not only meet user expectations but exceed them, thus promoting better interaction, satisfaction, and overall performance of digital systems. Even if you don't remember everything that has been said, I hope you will have retained the key points of this Jakob law summarized above.
Importance of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience in Today's Digital World
Unless you live in a digital desert, it is clear that today's digital landscape is characterized by increased competition and increasingly demanding users and that, if you have read this long article, the law of he Jakob Nielsen user experience is of paramount importance. This law, centered on proven principles of interface design, is essential for companies seeking to distinguish themselves through the quality of their user interactions. This is why this law is and remains a fundamental pillar of today’s digital world.
Whether through social networks, notifications, information, we all know that users' attention is constantly demanded, ensuring an optimal user experience is crucial to captivate and maintain user interest. With a focus on intuitive and responsive interfaces, Jakob's Law helps businesses create digital environments that effectively engage users . By encouraging the design of clear, understandable interfaces and thereby reducing the need for users to seek external support, the principles of the Law of User Experience can significantly decrease support costs for businesses, while increasing the user autonomy and satisfaction .
Should I also reiterate that with a well-designed user interface, consistent with the Nielsen principles, you can significantly improve conversion rates by simplifying user journeys and minimizing the friction that can lead to abandonment. Likewise, a good user experience is essential for customer retention, as it contributes to positive product perception and builds user loyalty .
One of Nielsen's key principles is to design for all users, including those with disabilities . By following this guideline, companies can ensure that their products are accessible to a wider range of people , which not only expands their market but also strengthens their social responsibility.
And what can we say about the impact on SEO and online visibility. As search engines continue to refine their algorithms to favor sites with excellent UX, adhering to the Nielsen Principles becomes a key factor in improving SEO . Sites that load quickly, are easy to navigate, and engage users rank higher, increasing visibility and organic traffic.
In summary, and this is one of the reasons we decided to write this comprehensive article, Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience offers essential guidelines for navigating today's complex digital ecosystem . By applying these principles, businesses can not only improve user experience but also realize tangible benefits such as increased conversions, reduced costs, and improved competitive positioning. These benefits demonstrate why Nielsen's Law remains an invaluable resource for designers and developers looking to optimize their digital products.
Encouragement to apply the principles of the law to improve user experience and SEO
Adopting the principles of Jakob Nielsen's Law of User Experience is not just a recommendation for improving the aesthetics or functionality of a user interface; it is an essential strategy for strengthening a company's competitiveness in the digital economy . The benefits of implementing this law extend beyond immediately improving user interaction, also influencing SEO, customer retention, and operational efficiency. Here are key aspects to encourage the application of these principles:
- Training and Awareness : To effectively integrate Nielsen principles, organizations must invest in training their design and development teams. This includes not only technical training on UX best practices but also workshops on the importance of user experience in the overall company strategy. Raising awareness across teams of the crucial role of UX can help align the efforts of all departments towards the common goal of improving the customer experience.
- Regular user testing : Application of Nielsen's Law principles should be supported by continuous user testing to evaluate the effectiveness of interfaces and identify areas requiring improvement. These tests allow us to collect direct feedback from users, which is essential for understanding their needs and behaviors. Iterative cycles of design, testing, and modification help refine the user interface to maximize its compliance with Nielsen principles.
- Integration of feedback into development cycles : For the application of Nielsen principles to be effective, feedback obtained through user testing must be quickly integrated into development cycles. This helps ensure that necessary adjustments are made proactively rather than reactively, reducing the time between identifying a UX issue and fixing it.
- Using Clear Success Metrics : Defining clear metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of UX improvements can help measure the impact of applying Nielsen principles. These metrics can include conversion rate, bounce rate, time on site, and user satisfaction score. By measuring these metrics before and after changes, businesses can concretely quantify the benefits of adopting Nielsen principles.
- Continuous Commitment to UX Improvement : Improving user experience is an ongoing process, not a once-and-for-all task. Businesses must commit to constantly maintaining and improving their interfaces in response to changing technologies, design trends, and user expectations. This commitment must be supported by a company culture that values UX and recognizes its impact on overall success.
By actively encouraging the adoption of these principles, my desire is to encourage companies to join the spirit of our development agency by explaining to them that they can not only improve the user experience but also benefit from a competitive advantage sustainable . This is crucial in a digital landscape where UX can determine the success or failure of a product.
References
Here are some references to case studies in English and French concerning Jakob Nielsen's Law which allowed me to write this article:
In English :
- " Jakob's Law in Web User Experience Design " by Raluca Budiu on the Nielsen Norman Group website: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/jakobs-law-web-ux/
This article provides an in-depth explanation of Jakob's Law and includes a case study of how the law was applied to improve the design of an e-commerce website. - “ How Jakob's Law Helps You Create a Great User Experience ” by Katie Sherwin on HubSpot: https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/jakobs-law
This article includes a case study on how Jakob's Law was applied to improve the design of an online travel website. - “ The Power Law of Learning: Consistency vs. Innovation in User Interfaces ” by Raluca Budiu on the Nielsen Norman Group website: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/power-law-learning/
This article demonstrates that for many tasks, learning curves show an initial period of learning, followed by a plateau of optimal efficiency. The new interfaces compete with the old, widely used ones, which have already reached this plateau.
In French :
- " Jakob's law, or how to improve the user experience thanks to conventions " by Jean-François Nogier on the Usabilis site: https://www.usabilis.com/blog/2017/10/04/la-loi-de -jakob-or-how-to-improve-user-experience-through-conventions/
This article provides a detailed explanation of Jakob's Law and includes a case study of how the law was applied to improve user design. 'a website of a financial services company. - " Jakob's law: a golden rule for the user experience " by Mathieu Chapon on the Webmarketing & co'm website: https://www.webmarketing-com.com/2017/01/25/59911-la -jakob-law-a-golden-rule-for-user-experience
This article includes a case study of how Jakob's Law was applied to improve the design of an online clothing company's website.
Sites :
Nielsen Norman Group Official Website : Nielsen Norman Group : This is the consulting site co-founded by Jakob Nielsen. There you will find many articles, research reports and case studies on usability and user experience. They regularly publish in-depth analyzes on various aspects of UX that apply or discuss Nielsen principles.
Academic Research :
- Google Scholar : For academic case studies, you can search Google Scholar using terms such as "Jakob Nielsen usability principles case study" or "Nielsen usability law case study". Here you'll find research articles that analyze the impact of Nielsen principles in real-world settings.
- ResearchGate : Another platform where researchers share their publications. There you can search for documents relating to the application of Nielsen laws in UX.
Books and Publications :
- Books by Jakob Nielsen : Jakob Nielsen has written several books that are references in UX. Titles like “Designing Web Usability” and “Usability Engineering” contain detailed discussions and case studies related to its principles.
- “Don’t Make Me Think” by Steve Krug : Although not directly related to Nielsen, this book is essential UX reading that nicely complements Nielsen principles with practical case studies.